Key Differences Between Electromechanical and Solid-State Relays
페이지 정보
작성자 Margery Garvin 댓글 0건 조회 15회 작성일 25-10-09 06:23본문
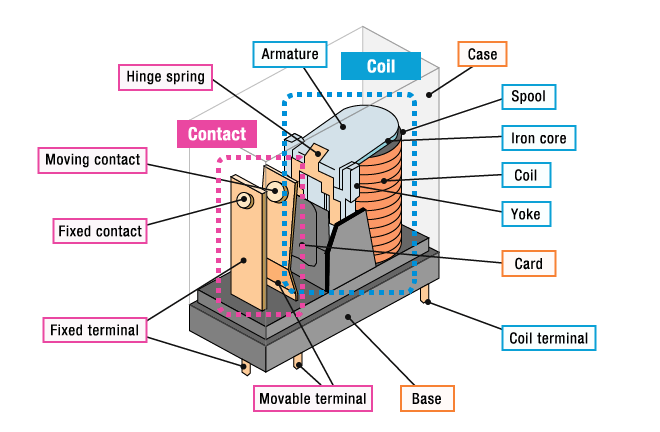
Electromechanical relays and solid-state relays are both used to switch electrical circuits on and off but they operate in fundamentally different ways. Electromechanical relays use physical moving parts—when an electrical signal is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts a metal armature to either close or open a set of contacts. Current transmission occurs via direct contact engagement.
The mechanical action produces a distinct click during operation and their contact surfaces gradually erode with use. Dust, humidity, and mechanical shock reduce their operational durability.
Solid state relays, on the other hand, have no moving parts and rely on semiconductor components such as thyristors, transistors, or triacs to switch the current. When a small control signal is applied, the switching occurs through semiconductor conduction states, enabling or interrupting the load current.
They operate completely quietly and offer superior long-term reliability. provide quicker response times and are immune to contact erosion and electrical sparking, انواع رله making them ideal for applications requiring frequent switching or high reliability.
They require thermal management during use and must be paired with thermal solutions to prevent overheating. They can also leak a small amount of current even when turned off, which poses risks in ultra-low-power or safety-sensitive circuits.
Although EMRs are not as fast or long-lasting typically ensure total isolation when deactivated and can handle higher surge currents without damage.
In terms of cost, electromechanical relays are generally cheaper upfront, but solid state relays may be more cost effective over the long term due to absence of mechanical wear and infrequent upkeep. The optimal selection hinges on system requirements.
In rugged, low-cycle, high-power environments, EMRs are the go-to choice.
SSRs excel in high-frequency, noise-sensitive, or precision environments like robotics, diagnostic equipment, and smart home devices.
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

